Chart of Global Forest

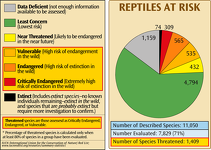
There are just under 40,000,000 sq. km of forest area remaining on Earth.
Of the remaining primary forests, only ~18% are in legally protected forests, which is approximately 5% of the original forest estimated to have covered the planet 8,000 years ago.
The FAO defines primary forests as naturally regenerated forests of native tree species where there are no clearly visible indications of human activity and the ecological processes are not significantly disturbed.
While ‘old-growth’ is a commonly used term for primary forest, there is no generally agreed definition of old growth or age of trees because age varies with site, regional and biome specific factors. While many primary forest trees are long lived (300-1500 years), old growth is generally defined according to the presence of specific forest structures including large, older trees, snags, coarse woody debris and canopy layering that take decades to centuries to acquire.
Sources
UN FAO State of the World’s Forest 2020, http://www.fao.org/3/ca8642en/CA8642EN.pdf
UN FAO Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020, Terms and Definitions; www.fao.org/3/I8661EN/i8661en.pdf;
Policy Options for the World’s Primary Forests in MultilateralEnvironmental Agreements, Mackey, et. al.;
https://openresearch-repository.anu.edu.au/bitstream/1885/66494/2/01_Mackey_Policy_Options_for_the_World%27s_2015.pdf
Text source: https://primaryforest.org/fact-sheets/fact-sheet-1-primary-forrest-introduction/
Tags: forest, biomes, ecology, deforestation, primary forest, old growth forest, global forest, global-ecology
Sign up for EARTH Dispatches
Enter you email below to get jaw dropping charts and maps delivered straight to your inbox.
Get the EARTH presentation
A 150 page high-resolution PDF containing all updated maps, charts and data on EARTH website; use as an information-packed educational slide show, printed booklet or a set of single-page handouts.
Learn More